In [Part 1], we laid a solid foundation for our AI-assisted workflow, covering everything from adopting the right mindset to project planning.
Now that we have a clear roadmap, it’s time to move on to the most exciting phase: building the project. In this part, we’ll explore how to leverage AI to write code, design databases, and automate documentation.
1. AI Code Generation: Turning Ideas into Reality

One of AI’s most incredible powers is its ability to turn natural language requests into code. Instead of spending hours typing out boilerplate code, AI can help you generate snippets, repetitive functions, or even entire components.
Remember the mindset we discussed in Part 1: AI is a collaborator, not a magic wand. Use AI to create the first “draft,” and then you’ll refine and optimize it.
Practical Prompts to Get You Started:

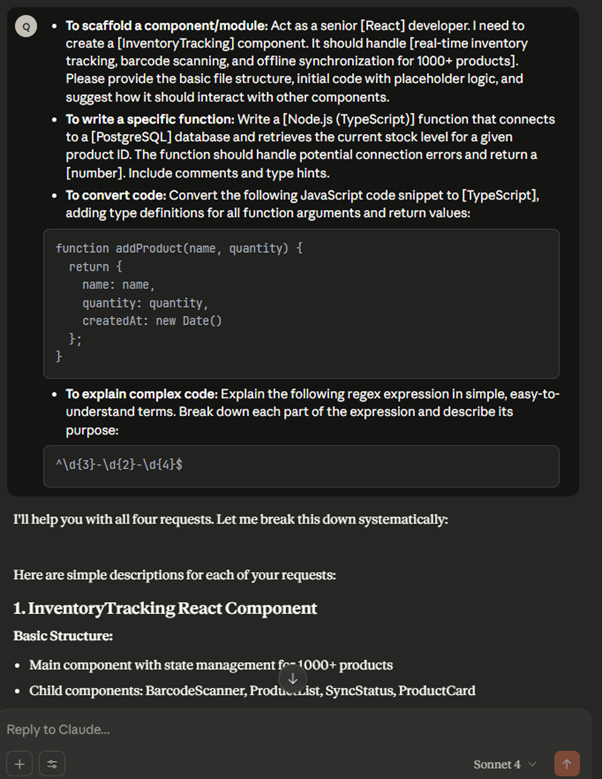
- To scaffold a component/module: Act as a senior [framework] developer. I need to create a [component name] component. It should handle [describe functionality]. Please provide the basic file structure, initial code with placeholder logic, and suggest how it should interact with other components.
- To write a specific function: Write a Python function that takes a URL as input, performs a GET request, and scrapes all image URLs from the HTML content. The function should handle potential connection errors and return a list of valid image URLs. Include comments and type hints.
- To convert code: Convert the following JavaScript code snippet to TypeScript, adding type definitions for all function arguments and return values: [paste JS code here].
- To explain complex code: Explain the following regex expression in simple, easy-to-understand terms. Break down each part of the expression and describe its purpose: [paste regex expression].
Pro Tip: When working with sensitive or proprietary company code, be careful about pasting it directly into the AI. It’s best to summarize the logic instead.
2. Database Design: Simplifying a Complex Task
Database design is a crucial step, and AI can be a powerful assistant. Instead of drawing diagrams from scratch, you can describe your requirements and let AI propose an initial design.
Prompt Examples:
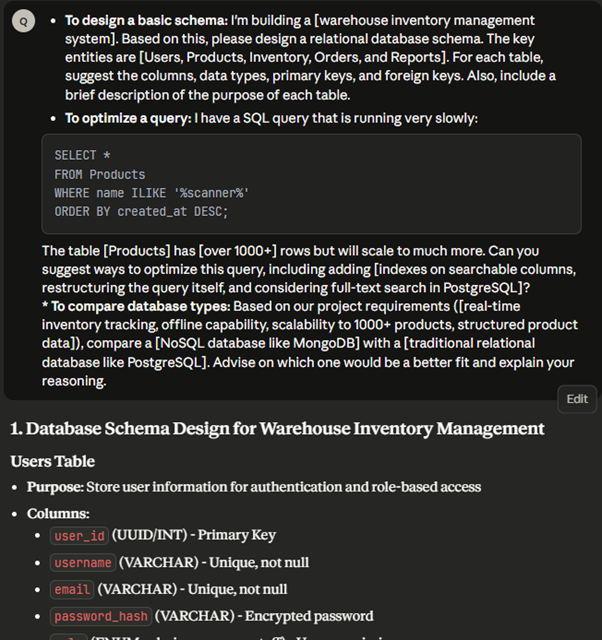
- To design a basic schema: I’m building an e-commerce platform. Based on this, please design a relational database schema. The key entities are Users, Products, Orders, and Reviews. For each table, suggest the columns, data types, primary keys, and foreign keys. Also, include a brief description of the purpose of each table.
- To optimize a query: I have a SQL query that is running very slowly: [paste query]. The table ‘products’ has a million rows. Can you suggest ways to optimize this query, including adding indexes and restructuring the query itself?
- To compare database types: Based on our project requirements (real-time data, high scalability, unstructured data), compare a NoSQL database like MongoDB with a traditional relational database like PostgreSQL. Advise on which one would be a better fit and explain your reasoning.
3. Documentation Automation: Reducing the Writing Burden
Writing documentation is often a time-consuming and unloved task. With AI, you can automate a significant portion of this work, ensuring your documentation is always up-to-date and comprehensive.
Prompt Examples:
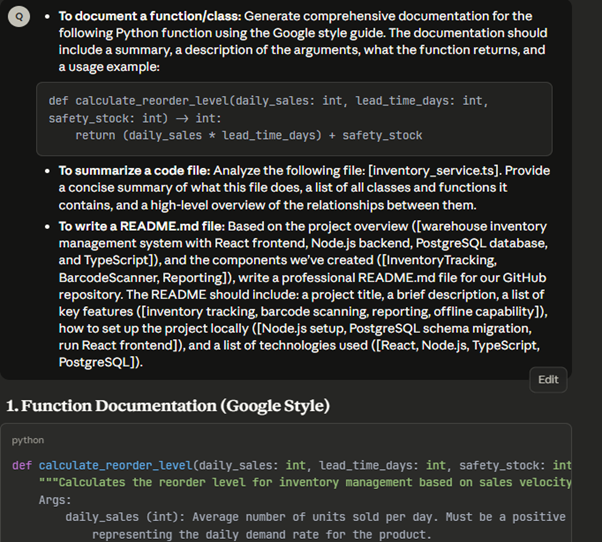
- To document a function/class: Generate comprehensive documentation for the following Python function using the Google style guide. The documentation should include a summary, a description of the arguments, what the function returns, and a usage example: [paste function].
- To summarize a code file: Analyze the following file: [paste code]. Provide a concise summary of what this file does, a list of all classes and functions it contains, and a high-level overview of the relationships between them.
- To write a README.md file: Based on the project overview and the components we’ve created, write a professional README.md file for our GitHub repository. The README should include: a project title, a brief description, a list of key features, how to set up the project locally, and a list of technologies used.
4. A Quick Checklist Before Wrapping Up the “Building” Phase
Check for security: Always review AI-generated code, especially sections related to security or sensitive data handling.
- Run tests: Never skip testing. Code from AI can still contain bugs.
Verify against the initial design: Compare what the AI generates with your roadmap and architecture from Part 1 to ensure everything stays on track. - Learn and save: If the AI provides a great solution, save both the prompt and the solution to your prompt library for future use.
Conclusion of Part 2
AI’s potential in the building phase is endless. It not only helps you work faster but also encourages you to experiment with new ideas with less risk.
In Part 3, we’ll explore how to Polish and Maintain a project, from automated testing and performance optimization to using AI for version control.
See you all then!








Vui lòng đăng nhập để bình luận.